
D Schematics of truncated B7-H3 (aa 1-258) with the N104 glycosylation site and 106-110SLRLQ motif for HSC70 binding, and AOL blots of the co-IP B7-H3 protein with wildtype N104 and N91Q/N189Q/N215Q mutations. C Co-IP assays showed the effects of FUT8 knockdown on the interaction between B7-H3 and HSC70 or LAMP2A. B Immunoblots of B7-H3 protein in SW480 and HCT-8 cells after knockdown of FUT8 and / or LAMP2A. FDW028, an inhibitor specifically targeted FUT8, promotes defucosylation and consequent HSC70/LAMP2A-mediated lysosomal degradation of B7-H3, and exhibits potent anti-mCRC activities.Ī Immunoblots of B7-H3 protein in SW480 and HCT-8 cells after knockdown of FUT8 and / or HSC70. Taken together, FUT8 inhibition destabilizes B7-H3 through CMA-mediated lysosomal proteolysis, and FDW028 acts as a potent therapeutic candidate against mCRC by targeting FUT8. FDW028 exhibits potent anti-tumor activity by defucosylation and impelling lysosomal degradation of B7-H3 through the CMA pathway. Then we report the development and characterization of a potent and highly selective small-molecule inhibitor of FUT8, named FDW028, which evidently prolongs the survival of mice with CRC pulmonary metastases (CRPM). FUT8-silence-induced defucosylation at N104 on B7-H3 attracts heat shock protein family A member 8 (HSPA8, also known as HSC70) to bind with 106-110 SLRLQ motif and consequently propels lysosomal proteolysis of B7-H3 through the chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) pathway. FUT8 mediates the core fucosylation of CD276 (B7-H3), a key immune checkpoint molecule (ICM), in CRC. Fucosyltransferase 8 (FUT8) is a potential therapeutic target with high level in most malignant cancers including CRC.
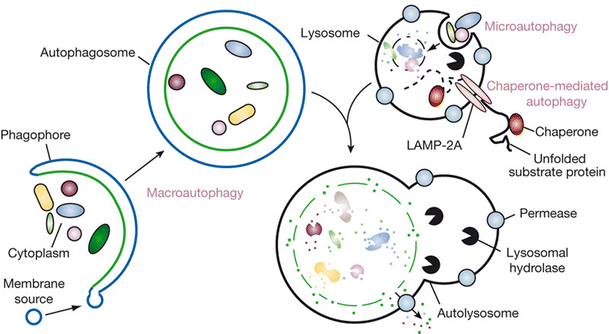
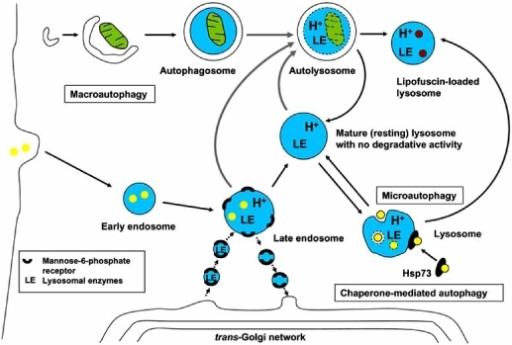
Thus, it is urgent to discover new drugs for mCRC. Metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) is a major cause of cancer-related mortality due to the absence of effective therapeutics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
